News
Original content
Global prices for tomato paste remained relatively stable heading into Aug-25. With the processing tomato harvest underway in key Northern Hemisphere regions such as California and Italy, the market has entered a watch-and-wait phase. Buyers are evaluating early crop outlooks before committing to major contracts, resulting in a temporary pricing equilibrium following a period of volatility. Final yields from these harvests will be the primary factor influencing price direction in the coming months.
The European processing tomato sector is closely watching trade developments from the United States (US) regarding proposed new tariffs. The potential for increased import duties on processed tomato products, such as sauces and canned tomatoes, could disrupt established trade flows between the two major markets. European exporters are concerned that such measures could impact their competitiveness in the US, a key market for high-value processed goods.
Researchers on Réunion Island have identified a new tomato-infecting virus, the Tomato yellow leaf curl Reunion virus (TYLCREV), in greenhouse crops in St. Louis and Le Tampon. The recombinant monopartite begomovirus combines genetic material from the widespread Tomato yellow leaf curl virus (52%) and tomato viruses from Madagascar (48%). While currently localized, its genetic makeup suggests potential for increased virulence and wider spread, mirroring past TYLCV outbreaks. Transmitted by whiteflies, TYLCREV poses a possible threat to regional and global tomato production, prompting calls for intensified surveillance.
Vestaron, a US-based agricultural technology company specializing in peptide-based bioinsecticides, has secured emergency use authorization in Greece for its product SPEAR® LEP. The approval targets the control of the highly destructive tomato leafminer (Tuta absoluta), a pest known for causing severe yield losses in tomato crops. This authorization expands SPEAR® LEP’s global reach, enabling use during Greece’s peak Tuta absoluta season. Its peptide-based mode of action controls pests without harming beneficial insects, offers zero MRLs, and supports compliance with strict EU pesticide regulations. Among recent emergency approvals in Europe, the product has also been authorized in Italy and Portugal for controlling other pests.
In an important strategic move for the European tomato industry, Italian processing giant La Doria announced its acquisition of competitor Feger in mid-July. This consolidation is poised to reshape the competitive landscape for processed tomato products, particularly in the private label and co-packing segments. The move reflects a broader trend of consolidation as companies seek greater scale and efficiency to navigate volatile input costs and global competition.
The harvest season for processing tomatoes in California began in early July and ramped up by the end of the month. As of August 3, weekly tonnage is being closely monitored. The industry is increasingly leveraging artificial intelligence (AI)-powered forecasting tools to improve yield predictions and manage logistics as the season progresses. These technologies are becoming essential for optimizing the supply chain amid growing climate variability.
.png)
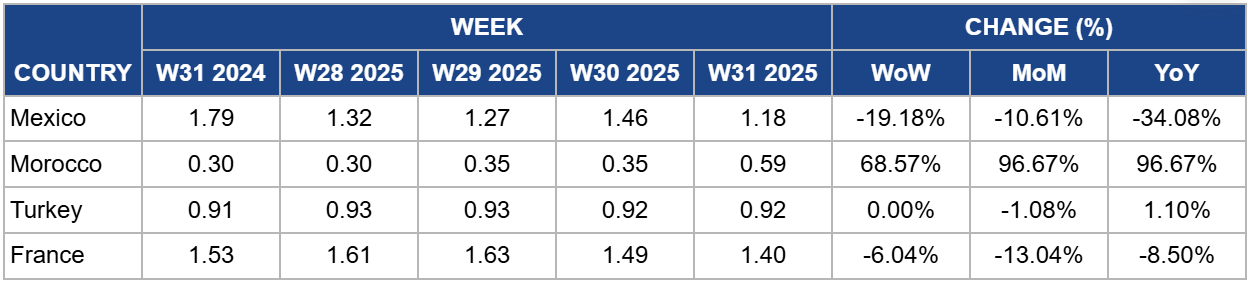
In W31, wholesale tomato prices in Mexico dropped 19.18% week-on-week (WoW), falling to USD 1.18 per kilogram (kg). This decline is primarily attributed to stable supply from key growing regions and slightly reduced demand from the US market, as domestic production increases in some states. Despite the weekly decrease, prices remain volatile, influenced by ongoing trade shifts driven by tariff implementation and variable weather patterns. Prices are down 34.08% year-on-year (YoY), reflecting the higher price levels seen during the same period last year. In 2024, wholesale prices were at 1.79/kg, much tighter due to an intense heatwave that severely impacted production volumes.
Moroccan tomato prices surged by 68.57% WoW, reaching USD 0.59/kg in W31. This sharp increase signals the tail end of Morocco's primary export season to Europe. With lower volumes available for export, reduced supply has driven prices up significantly. While end-of-season tightening is typical, the effect has been particularly pronounced this week, resulting in a near doubling of prices, up 96.67% month-on-month (MoM) and YoY.
In W31, Turkish tomato prices remained stable, holding at USD 0.92/kg. This stability reflects a well-balanced market, with steady supply from the summer harvest meeting consistent domestic and regional export demand. Additional, favorable growing conditions have supported a consistent output, preventing any significant price fluctuations. Prices are almost identical to the same period last year, indicating a period of equilibrium in the Turkish market.
French tomato prices decreased by 6.04% WoW to USD 1.40/kg in W31. This price drop is a result of increasing domestic supply as the peak of the French summer harvest reaches the market. After earlier reports of weather-related delays, production volumes have now recovered, easing the supply constraints that had previously supported higher prices. The current price is 8.50% lower YoY, suggesting more robust domestic availability in 2025 compared to 2024.
European tomato processors facing potential US tariffs should proactively diversify their export portfolios. This involves strengthening trade relationships with non-US markets such as Canada, Japan, and growing economies in the Middle East. Investing in market research to tailor products (e.g., specific packaging, sauce formulations) to new regional tastes can mitigate the risk of over-reliance on the US market and buffer against trade policy shocks.
The emergency authorization of a new bioinsecticide in Greece signals a critical market need across Europe for effective alternatives to traditional pesticides. Rising pest resistance and regulatory pressures are creating strong, unmet demand from growers for innovative crop protection. Agricultural input suppliers and ag-tech firms should accelerate the registration and promotion of novel, sustainable pest management solutions, as offering products with new mechanisms of action provides a significant competitive advantage in this evolving landscape.
The emergence of the TYLCREV virus should be monitored by seed companies, ag-tech firms, and large-scale producers. Investment in research for resistant cultivars and rapid diagnostic tools should be a long-term priority to safeguard future production from this and other emerging phytosanitary threats.
Sources: Tridge, Tomato News, Ladoria Group, Lupa Foods, Foodmate
Read more relevant content
Recommended suppliers for you
What to read next